Based on various factors like location, surface relief, upper air circulation etc. the climate of any country broadly falls in one out of many climatic Zones.
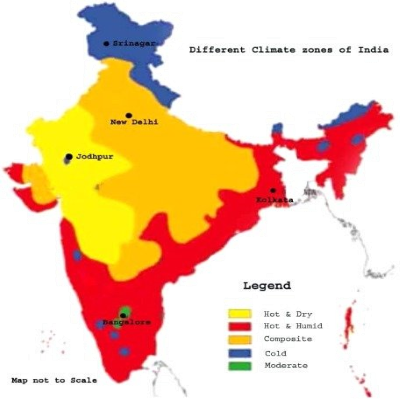
Climate of India cannot be categorized in one climatic Zone due to its largeness and diversity of geography and geology across different parts of the country.
As India lies above equator, most of Southern India falls in temperate climate zone and the Peninsular India witnesses Maritime Climate due to closeness of sea on all three sides.
The climate of India is deeply influenced by the Himalayas and the Thar Desert. Himalayas in the North act as barrier to cold winds from Central Asia keeping Northern India warm and only slightly cool during winters, much warmer as compared to other countries on the same latitude.
The climate of India is deeply influenced by the Himalayas and the Thar Desert. Himalayas in the North act as barrier to cold winds from Central Asia keeping Northern India warm and only slightly cool during winters, much warmer as compared to other countries on the same latitude.
The Thar Desert plays a significant role in gathering a huge amount of rainfall for the country by absorbing the South West Monsoon winds.
This unique geographical condition gives India the peculiar weather with two monsoon seasons with hot and cold weather seasons. In all India have forests; glaciers with rivers flowing from them, also fog, snow, thunder, and hail form an integral part of India’s climate.
Climatic Regions of India
Usually the geography of a country divides it into a Climatic Zone, but considering the vastness and variety in India’s geology and geography it is divided in Four Climatic Regions or groups which can further be divided in seven climatic types.- Tropical rainy climatic group
1.1> Tropical monsoon rain forest
1.2> Tropical wet and dry climate - Dry climate group
2.1> Tropical semi-arid steppe climate
2.2> Tropical and sub-tropical steppe - Humid sub-tropical climate group
3.1> Humid sub-tropical with dry winters - Mountain climate
Cold temperature with increase in altitude
Seasons
India experiences a wide range of climatic conditions due to different geography and geology throughout different parts of the country. India is a tropical country of sub continental size, peninsular in shape and has extensive coastline on three sides. Antarctica happens to be the next door neighbor on the south. Himalayas is making a tallest wall towards north.This unique geographical condition gives India the peculiar weather with two monsoon seasons with hot and cold weather seasons. In all India have forests; glaciers with rivers flowing from them, also fog, snow, thunder, and hail form an integral part of India’s climate.
These seasons include in India:
- Vasant Ritu(Spring)
- Grishma Ritu(Summer)
- Varsha Ritu(Monsoon)
- Ritu(Autumn)
- Hemant Ritu (Pre-Winter)
- Shishir Ritu (Winter)




