What we see today, is the outcome of all those political influences upon its geography. It covers an area of 3,287,590 sq. km and stretches from the Himalayas in the north to Kanyakumari in the south.
Neighbours of India
India is surrounded by Afghanistan and Pakistan to the north-west; China, Bhutan and Nepal to the north; Myanmar to the east; and Bangladesh to the east of West Bengal while Sri Lanka is separated from India by a narrow channel of sea, formed by Palk Strait and the Gulf of Mannar. The Line of Actual Control (LAC) divides India with China and covers a stretch of 4,057kms.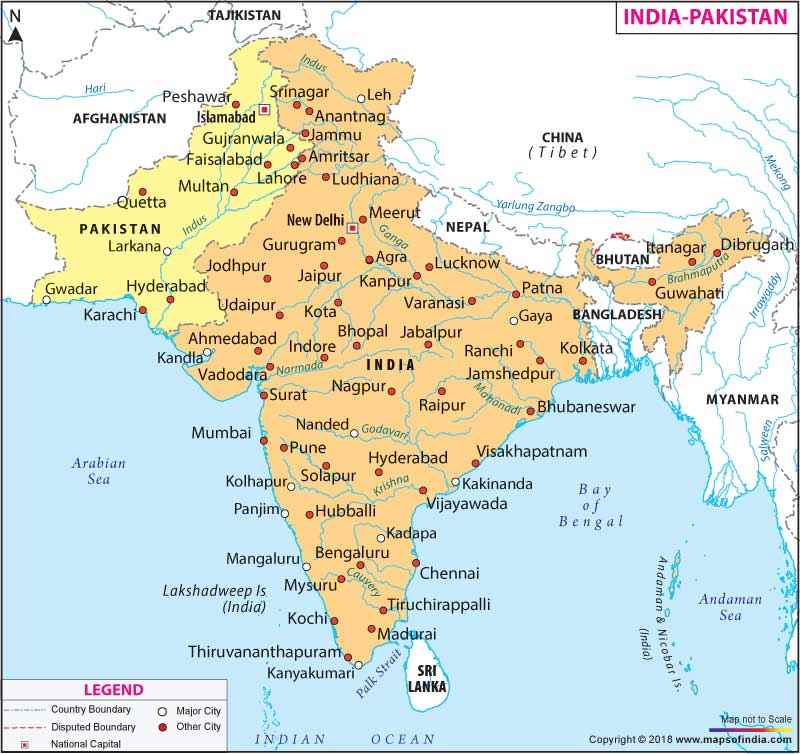
India-Pakistan Border
India shares its western borders with Pakistan which is about 3000 kms long, stretching from Jammu & Kashmir, Punjab, Rajasthan to Kutch region of Gujarat. The Line of Control (LoC) is the most perilous border that slices Kashmir into Jammu-Kashmir of India and Azad Kashmir of Pakistan.Punjab is divided into Indian state of Punjab and Punjab of Pakistan through the Wagah line. Gujarat and Rajasthan are separated from Pakistan’s Sindh area through the Zero Point. Moving towards the south, the border runs from Manora Island of Pakistan to Mumbai Harbor of India.
These borders were traced through the Radcliffe line which was outlined when India was politically divided in 1947. The line got its name from architect Sir Cyril Radcliffe, who had created it during the partition.
These borders were traced through the Radcliffe line which was outlined when India was politically divided in 1947. The line got its name from architect Sir Cyril Radcliffe, who had created it during the partition.
India-China Border – The MacMohan Line
India and China are separated by McMohan Line which is named after the foreign secretary of British-led Government in India. Since 1950s, the border continues to stay a matter of controversy which runs along the states of Uttarakhand, Sikkim, Arunachal Pradesh, Jammu and Kashmir and Himachal Pradesh.India-Bangladesh Border
India and Bangladesh are separated by the world’s fifth longest border that is 3909 kms long and touches Indian states of West Bengal, Meghalaya, Assam Mizoram and Tripura. India has its 106 enclaves in Bangladesh while there are 92 Bangladeshi enclaves in India.In September 2011, a strip Teen Bigha Corridor that was earlier a part of India, was opened to Bangladeshi people so that they could ingress their way to their enclaves namely, Dehgram and Angalpota.
Politically Apart, Culturally Conjoined
Owing to common historical background as well as geographical conditions, territories surrounding these political borders from both the sides look interwoven culturally and socially. They practice the blended lifestyle despite carrying different national identities.
Borders within States of India
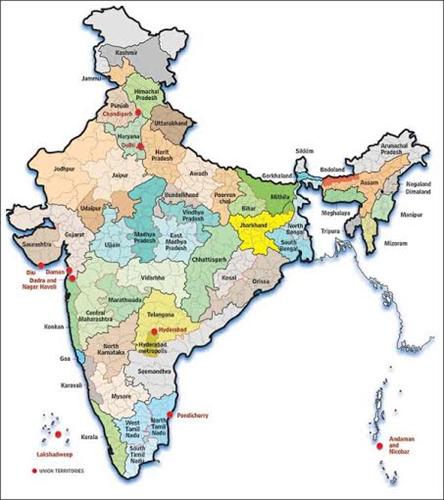
During the British rule, India was divided into the provinces under the British government directly, and princely states which were still ruled by the local rulers under the governance of the British.
India-Burma Border
The Indo-Burma border is 1624 kms long along which a border barrier is being created by Indiato seal the border. Nagaland, Manipur, Mizoram and Arunachal Pradesh share the border with Burma.India-Nepal Border
The border with Nepal traverses 1,751 km and shares with the Indian states of Bihar, Uttarakhand, Sikkim, Uttar Pradesh and West Bengal.Politically Apart, Culturally Conjoined
Owing to common historical background as well as geographical conditions, territories surrounding these political borders from both the sides look interwoven culturally and socially. They practice the blended lifestyle despite carrying different national identities.
Borders within States of India

During the British rule, India was divided into the provinces under the British government directly, and princely states which were still ruled by the local rulers under the governance of the British.
During independence, when the division of the nation happened, these princely provinces were distributed amongst Pakistan and India. The Constitution of India was implemented on January 26, 1950 and India became a ‘Union of States’.
A lot of changes have taken place, many new states have formed since then. Today there are twenty-eight states and eight union territories, which are further divided into districts or Zilas, India is divided into. These states are Punjab, Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Uttaranchal, Uttar Pradesh, Rajasthan, Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Goa, Kerala, Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh, Odisha, West Bengal, Bihar, Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, Telangana, Sikkim, and Tripura. The Union territories are Chandigarh, National Capital Territory of Delhi, Dadra and Nagar Haveli & Daman and Diu, Jammu and Kashmir, Ladakh, Lakshadweep, Puducherry and Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
Chhattisgarh, the state in Central India was carved out from Madhya Pradesh in November 2000. The state borders with Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Telangana, Andhra Pradesh, Odisha, Jharkhand and Uttar Pradesh. The idea about its creation was proposed long time back in 1924, for the first time.
A lot of changes have taken place, many new states have formed since then. Today there are twenty-eight states and eight union territories, which are further divided into districts or Zilas, India is divided into. These states are Punjab, Haryana, Himachal Pradesh, Uttaranchal, Uttar Pradesh, Rajasthan, Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Goa, Kerala, Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh, Odisha, West Bengal, Bihar, Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, Arunachal Pradesh, Assam, Manipur, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland, Telangana, Sikkim, and Tripura. The Union territories are Chandigarh, National Capital Territory of Delhi, Dadra and Nagar Haveli & Daman and Diu, Jammu and Kashmir, Ladakh, Lakshadweep, Puducherry and Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
Creation of New States
Before Aug. 5, 2019, India had 29 states and seven Union Territories (UTs). The country now has only 28 states since Jammu and Kashmir has been converted. The country now has 8 UTs with Jammu and Kashmir as one new entrant and Ladakh as the other.
But the matter never materialized as the proposals were dissolved following meetings and strikes and in 1954, the state Reorganization Commission was established.
The proposal was out forward again and again, especially in 1990s the matter took a strong hold, being supported by all political parties including the major ones like Congress and BJP. On August 25, 2000 the government of India finally consented to the proposal and the state was formed on November 1, 2000.
Uttarakhand, popular as the ‘Land of Gods’ got a separate identity as a state on November 9, 2000 when it was separated from Uttar Pradesh.
Uttarakhand, popular as the ‘Land of Gods’ got a separate identity as a state on November 9, 2000 when it was separated from Uttar Pradesh.
It shares its borders with Uttar Pradesh and Himachal Pradesh, Tibet and Nepal. The state is further divides into two regions namely, Garhwal and Kumaon along with 13 districts.
Jharkhand was extracted from the Indian state of Bihar on November 15, 2000. The state shares its borders with Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Odisha and West Bengal.
Jharkhand was extracted from the Indian state of Bihar on November 15, 2000. The state shares its borders with Bihar, Uttar Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Odisha and West Bengal.
The demand for its separate entity was raised as early as 1900 by a hockey player Jaipal Singh. The matter stayed pending for quite a long time until August 2, 2000, when the Bihar Reorganization Bill was passed by the government, thereby leading to the creation of 28th state of India.
Telangana used to be the princely areas of Hyderabad of Andhra Pradesh, that were earlier ruled by Nizams. Before it got a separate identity, there happened many protests, strikes that demanded the state-division.
Telangana used to be the princely areas of Hyderabad of Andhra Pradesh, that were earlier ruled by Nizams. Before it got a separate identity, there happened many protests, strikes that demanded the state-division.
On February 2014, the Andhra Pradesh Reorganization Act 2014 was passed by the government. Telangana became a separate state officially, on June 2, 2014 sharing the capital Hyderabad with Andhra Pradesh. It is bordered with Andhra Pradesh, Maharashtra, Karnataka and Chhattisgarh.
The Coastal Borders in India
The Indian seacoast spreads across 7000 kms, from western coastal plain to eastern coastal plains. The eastern coastal plain stretches from Tamil Nadu to West Bengal. The western coastal plain lies between the Western Ghats and Arabian Sea spreading through the states Maharashtra, Goa, Karnataka and Kerala.It is divided into Konkan and Malabar Coast. The Indian coastal plains are washed by the Indian Ocean which also touches other continents – Africa and Australia.
India is a prodigious nation in many aspects. Its vastness has been realized by the enormous political developments that it has been witnessing since ages. A lot has been churning, and is expected in future.
India is a prodigious nation in many aspects. Its vastness has been realized by the enormous political developments that it has been witnessing since ages. A lot has been churning, and is expected in future.




