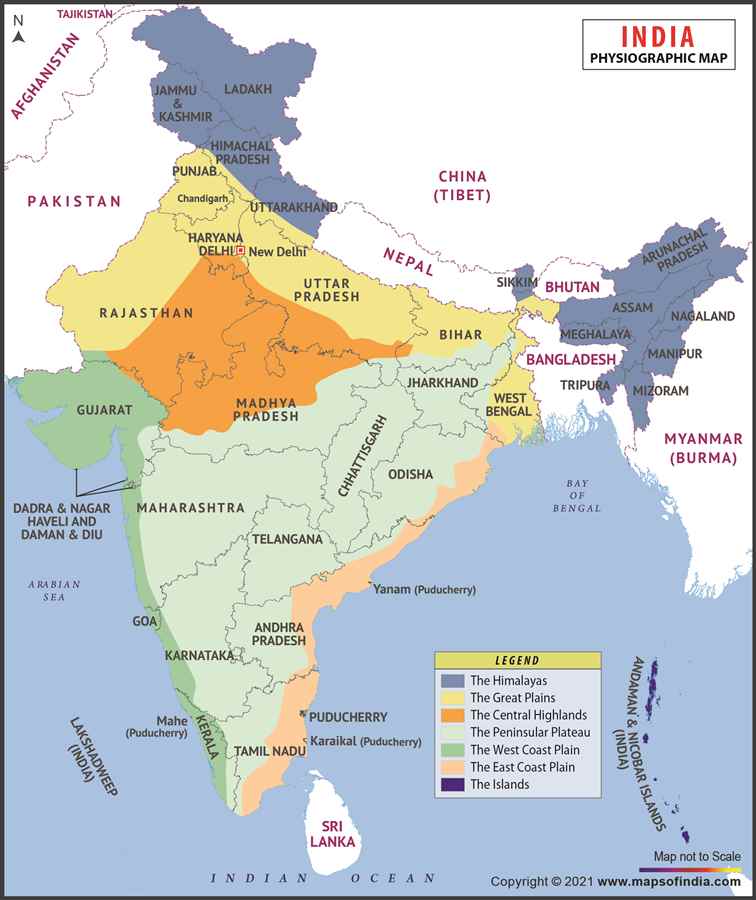
India comprises vast diversity in its topography, climate soils and vegetation. The country presents huge varieties of landforms from deep valleys to lofty mountains and dry deserts to water sheds.
The Tropic of Cancer 23° 30 ' N divides India almost into two halves. Indian peninsula tapers southward and divides Indian Ocean into two expanse of water - the Bay of Bengal and the Arabian Sea.
| Continent | Asia | ||
| Location | Southern Asia | ||
| Total Area | 3.28 million sq km | ||
| % of world’s Area | 2.42 % of total geographic area of world | ||
| Position | Seventh largest country in the world | ||
| Latitude | 8° 4 ' N and 37° 6' North | ||
| Longitude | 68° 7 ' and 97° 25 ' East | ||
| Hemisphere | Northern | ||
| Stretch | 3214 km from north south between extreme latitudes 2933 km from east to west between extreme longitudes | ||
| Land Frontier | 15, 200 km (90.44%) | ||
| Coast Line | 7, 500 km (9.56 %) | ||
| Neighboring countries | Bhutan, Burma, China, Nepal and Pakistan | ||
| Bounding water bodies | Arabian Sea (West) Bay of Bengal (East) Indian Ocean (South) | ||
| Main Islands | Lakshwadeep Islands in Arabian Sea Andaman & Nicobar Islands in Bay of Bengal | ||
| Elevation extremes Highest point Lowest point | Kangchenjunga 8,586 m (28,169.3 ft) Kuttanad -2.2 m (-7.2 ft) | ||
| Longest river | Ganges–Brahmaputra | ||
| Largest lake | Chilka Lake | ||
| Maritime claims | Contiguous zone: 24 Nautical Mile (NM) Continental Shelf: 200 Nautical Mile (NM) | ||
| Exclusive Economic Zone | 200 Nautical Miles (NM) | ||
| Territorial Sea | 12 Nautical Miles (NM) | ||
| Climate | Tropical monsoon in south Temperate climate in the north | ||
| Terrain | Himalayas in north Deccan Plateau in south Deserts in west Flat to rolling plain along the Ganges |
The Tropic of Cancer 23° 30 ' N divides India almost into two halves. Indian peninsula tapers southward and divides Indian Ocean into two expanse of water - the Bay of Bengal and the Arabian Sea.




