Today, the proud nation is one of the greatest and the largest democracy in the World and an unmissable name in the list of economic giants.

It is unimaginable, rather larger-than-life that from being a British colony, India has reached a position where it recently carried through the successful commercial launch of five British satellites.
It is an indisputable fact that political effectiveness and efficient political leaders of India play a crucial role in the rapid growth of this country.
The political journey of India is filled with twist and turns and formations and breakdowns. Find below a complete coverage of important political events in India or Political Chronology of India in the order of their occurrence.
Indian Politics
Political Parties in India
1858 - India comes under the direct dominion of the British crown
1885 - Indian National Congress (INC) was founded on December 28, 1885
1876 - The 'Empire of India' was formally established by the Prime Minister of the United Kingdom Benjamin Disraeli (first Earl of Beaconsfield) for Queen Victoria.
1920-22 - Mahatma Gandhi launches 'Non-cooperation' movement, an important phase of the Indian independence movement
1930 - The Dandi March (Salt Satyagraha), launched by Mahatma Gandhi begins with the Dandi march

1942-43 - Mahatma Gandhi launches 'Quit India' movement also known as India August Movement (August Kranti)
1944 - Subhas Chandra Bose (Netaji) calls Mahatma Gandhi as the 'Father of the Nation'
1947 - 15th August, End of British rule, a series of peaceful non-cooperation movements comes to a conclusion forcing the British to concede India's freedom. Pandit Jawaharlal Nehru assumed office as the first Prime Minister of India, and picked out fifteen other members for the First Nehru ministry

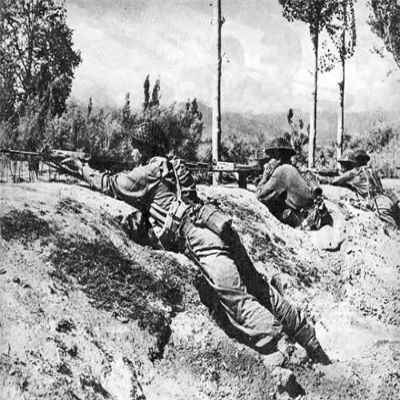
1947 - Indian defence of the Kashmir also known as Indo-Pakistani War of 1947 started(22 October 1947), the first attack took place at Thorar (a town in Poonch District) on October 3-4
1948 - The father of the nation, Mahatma Gandhiji was assassinated on January 30, 1948 at 5:17 PM, he was outside on the steps of a building where a prayer meeting was going to take place.

1949 - The First Kashmir War (Indo-Pakistani War of 1947-1948) came to an end, a formal truce was announced at 23:59 on the night of 1-2 January 1949
1949 - The Constituent Assembly took up the Constitution of India, blueprinted by a committee led by Babasaheb B. R. Ambedkar (Bhimrao Ramji Ambedkar)
1950 - India became a self-governing, democratic, republic after the Constitution of India came into effect on 26 January.

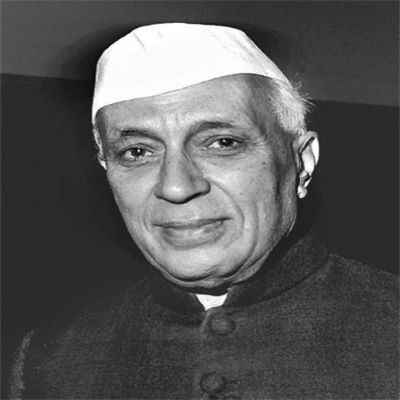
1951-52 - The Indian National Congress (INC) led by Jawaharlal Nehru won the first Indian General Election which elected the first Lok Sabha since India became independent. Nehru became the first (democratically) elected Prime Minister of India
1957 - Jawahar Nehru headed Indian National Congress (INC) comfortably won a second term, winning 371 of the 494 Lok Sabha seats
1959 - Indira Gandhi became the President of the Indian National Congress, which evoked dislikes for supposed favoritism, following which Jawaharlal Nehru had rejected her election
1962 - Jawaharlal Nehru led Congress won the third consecutive general election, winning 361 of the 494 Lok Sabha seats. On 20 October marks the beginning of the Sino-Indian Border Conflict which lasted until 21 November. Indian learned a valuable lesson and realized the need to beef up the defense force.

1964 - On 26 May, Nehru complained of back pain and had a brief conversation with doctors, before collapsing. The "architect" of modern India remained unconscious until his last breath. Gulzarilal Nanda was appointed as the first interim Prime Minister of India. K. Kamaraj turned the president of the INC and was instrumental in bringing Lal Bahadur Shastri as the third Prime Minister of India
1965 - The Indo-Pakistani War of 1965, fought over Kashmir. The belligerencies ended after a truce was declared following the intervention by the Soviet Union and United States of America
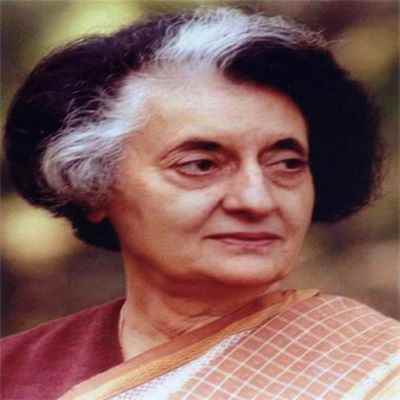
1966 - Lal Bahadur Shastri died soon after signing the Tashkent Declaration (a peace treaty between India and Pakistan). Gulzarilal Nanda (once again) assumed the role of interim Prime Minister. Indira Gandhi became the 4th Prime Minister of India.
1967 - Indira Gandhi was ousted from the Indian National Congress, which resulted in the formation of the Indian National Congress (R)
1971 - The newly formed Indian National Congress (R), led by Indira Gandhi won the Indian General Election 1971, winning 352 seats out of 518 Lok Sabha seats
1971 - Twenty year "Indo-Soviet Treaty of Peace, Friendship and Cooperation" was signed
1971 - Indo-Pakistani War of 1971, lasted for 13 days and resulted in a decisive Indian victory after the military forces of Pakistan signed the 'Instrument of Surrender'

1974 - On 18 May, India detonated the first nuclear bomb explosion (Pokhran-I) code named "Smiling Buddha" in Rajasthan
1975 - Prime Minister Indira Gandhi unilaterally had "the emergency" declared, after being found guilty of election misconduct by the Allahabad High Court. Thousands of political opponents were jailed.

1977 - On 23 March, the emergency was officially terminated and Mrs. Gandhi called for fresh elections. For the first time in Indian history, the Congress party lost the 1977 Indian General Election, winning only 189 seats out of 542 Lok Sabha seats. Morarji Desai became the 5th Prime Minister of India
1979 - Moraji Desai's government collapsed in just two years due to internal conflicts and Charan Singh assumed office as the 6th Prime Minister of India
1980 - Indira Gandhi comes back to power heading Indian National Congress (Indira), winning 374 seats out of 542 Lok Sabha seats (Indian general election, 1980).
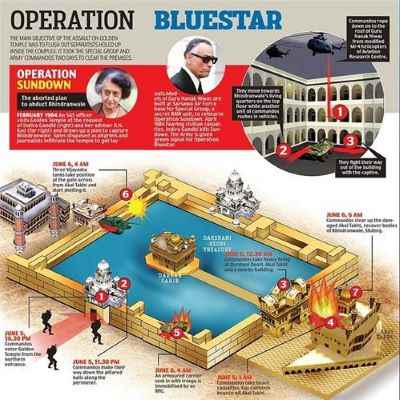
1984 - Operation Blue Star (June 3 and June 8), ordered by the Prime Minister Indira Gandhi, was set in motion to remove Jarnail Singh Bhindranwale (a Sikh Freedom Activist) and his supporters from the Amritsar Golden Temple (Harmandir Sahib Complex)
1984 - On 31 October, Mrs. Gandhi was assassinated by guards, following which her son, Rajiv Gandi, takes over. Soon after assuming office, Rajiv Gandhi called for fresh elections. Rajiv Gandhi won the Indian General Election 1984, winning 267 seats out of 533 Lok Sabha seats

1987 - Indian intervention in the Sri Lankan Civil War - commencement of Indian peacekeeping operation in the neighboring Democratic Socialist Republic of Sri Lanka
1989 - Rajiv Gandhi led Indian National Congress turned a loss in the Indian General Election and V. P. Singh of Janata Dal assumed office as the 8th Prime Minister of India.
1990 - Chandra Shekhar quit from the Janata Dal along with 64 MPs and floated a new political party called as Samajwadi Janata Party (SJP), and assumed office as the 9th Prime Minister of India
1991 - (Indian general election, 1991) just a day after the first phase of polling, Rajiv Gandhi was assassinated while campaigning at Sriperembudur. The election results led the Indian National Congress to form a minority government. P. V. Narasimha Rao became the 10th Prime Minister of India. Several economic reforms were implemented by the newly formed government

1992 - A massive number of Hindu extremists demolished the 16th-century Babri Masjid in Ayodhya, Uttar Pradesh, which resulted in religious tension across the nation
1996 - The year mark the most unstable period of Indian politics. The election results gave unclear mandate to any party. The president invited the Bharatiya Janata Party was the largest party in the Lok Sabha. Atal Bihari Vajpayee became the 11th Prime Minister of India. The newly formed government did not last long as the BJP government fell in just 13 days. With the outside support of the INC, H. D Deve Gowda of the Janata Dal party became the 12th Prime Minister of India
1997 - Janata Dal and many other smaller parties collectively called as United Front was in power for 18 months before handing over the government to a new leader from Janata Dal. I. K. Gujral became the 13th Prime Minister of India, with the support of Congress
1998 - Exactly after 332 days, with Congress backing out from extending support to the I. K. Gujral government, the country had the Indian general election, 1998. Though, BJP led by Vajpayee formed the government, it again collapsed after the All India Anna Dravida Munnetra Kazhagam (AIADMK) of Tamil Nadu backed out from supporting BJP
1999 - On February 19, Atal Bihari Vajpayee took a historic bus trip to Islamic Republic of Pakistan to meet his counterpart Nawaz Sharif and to sign a bilateral agreement called as Lahore Declaration
1999 - Kargil War - Tension gripped the Kashmir, which resulted in a brief state of war (Operation Vijay) with Pakistan in Kargil. India regains possession of Kargil and the Indian army made sure the complete eviction of interlopers

2000 - The 42nd President of the United States Bill Clinton makes a groundbreaking visit to India to diversify the engagement and emphasize the range of India-US relationship
2001 - Prime Minister Atal Bihari Vajpayee meets Pakistan President Pervez Musharraf in more than two years. The meeting concluded without a breakthrough because of conflicts over Kashmir

2002 - India achieved a massive success in test firing a nuclear-capable ballistic missile called as the Agni. Pakistan replied with its own nuclear warheads. The friendly ties hit a new low. A new war looked close at hand
2004 - On May, the ruling BJP and its alliance National Democratic Alliance (NDA) conceded vote out and the INC comes back to power. Manmohan Singh, an esteemed economic expert became the 14th Prime Minister of India with Sonia Gandhi being the INC president

2005 - To improve the ties, bus services from Srinagar to Muzzaffarabad in Pakistan-occupied Kashmir (PoK)
2006 - The largest-ever rural jobs scheme of India was established, proposed at elevating around 60 million family units out of poverty
2006 - India and US signed a nuclear understanding during a visit of the President George W. Bush. The United States of America extends access to India to civilian nuclear engineering, while India corresponds to the more eminent examination for its nuclear plans
2006 - The Chinese President Hu Jintao's visit to India stands for a significant milestone in bilateral relations and gave a huge boost to the Sino-Indian relations
2007 - India and Pakistan signed an accord proposed at abbreviating the danger of inadvertent atomic war
2007 - Manmohan Singh led government established its most substantial economic growth figures for twenty years at 9.4 percent
2007 - Pratibha Patil, the 12th President of India becomes first woman president of India

2008 - The United Progressive Alliance (UPA), the ruling coalition won the confidence vote in the Lok Sabha after leftist political parties backed away from supporting over the India-US nuclear cooperation deal
2008 - After the United States Congress's favorable reception, President George W. Bush signed an agreement, which ended the thirty year banning of nuclear trade with India
2009 - India and Russia signed businesses worth $700m, which enabled India to receive Uranium from the Russian capital
2009 - Indian General Election held to elect the 15th Lok Sabha was won by the UPA led by the Indian National Congress and Manmohan Singh was chosen for his second term as the Prime Minister of India
2009 - The newly formed UPA government gave a go-ahead for the formation of the new Indian state of Telangana (carved out of the Andhra Pradesh)
2010 - The Allahabad High Court delivered a historic rule that the sacred site of Ayodhya should be shared between Hindus and Muslims

2011 - Census 2011 showed the population of India at 1.21 billion
2011 - Anna Hazare, a prominent social activist staged 12-day hunger strike in Delhi protesting corruption
2011 - 2G spectrum scam took the center stage
2012 - Mohammad Ajmal Amir Qasab, the Pakistani militant who was captured alive during the 2008 Mumbai attacks was put to death in Pune prison
2014 - The Indian General Election of 2014, the largest election the world has ever seen, resulted in the National Democratic Alliance led by the Bharatiya Janata Party coming to the power with a majority. Narendra Modi became the 15th Prime Minister of India

2015 - Aam Aadmi Party (AAP), led by Arvind Kejriwal, hits the jackpot with a stunning victory in Delhi state elections, causing a major setback for the BJP after winning the 2014 general elections
2015: India and Bangladesh swap more than 160 enclaves. India invites US President Barack Obama to be the chief guest at the Republic Day parade, the first time a US president is invited to the event.
2016: Pradhan Mantri Ujjwala Yojana (PMUY) was launched to provide LPG connections to women below the poverty line without upfront charges. The BJP makes inroads in the northeast and forms government in Assam. Government announces demonetization of Rs500 and Rs1000 notes. More than 99 percent of 500- and 1,000-rupee notes were successfully returned and replaced, which indicated that even black money was successfully replaced despite the hurdles.
2017: The goods and services tax was introduced on 1 July. The BJP creates history with a landslide win in the Uttar Pradesh assembly election. General and railway budgets were presented together for the first time. The centralized consumption tax regime known as the Goods and Services Tax (GST) was implemented.
2019: The BJP government introduced the Citizenship Amendment Act in 2019, sparking widespread protests. On 5 August 2019, the Parliament of India voted in favor of a resolution tabled by Home Minister Amit Shah to revoke the temporary special status, or autonomy, granted under Article 370 of the Indian Constitution to Jammu and Kashmir—a region administered by India as a state which consists of the larger part of Kashmir. The government in August 2019, announced a merger of ten public sector banks into four. One of the benefits of consolidation is higher operational efficiency gains to reduce the cost of lending according to the official presentation made at the time of announcing the merger.
2020: In February 2020, riots broke out in Delhi. The Citizenship Amendment Act protests have been described as an instigating factor. Tensions escalated on the Indo-China border after aggressive skirmishes between Indian and Chinese troops beginning on 5 May 2020. The Rama Janmabhoomi temple construction officially started again after a Bhoomi Poojan ceremony on 5 August 2020. The trend of protests continued in 2020, with the 2020 Indian agriculture Act which sparked the Indian farmers' protest in August 2020. The farm laws which sparked year-long protests from Arhtiyas in Punjab and farmers in Haryana have been repealed in the Lok Sabha.
2020- Jammu Kashmir: The BJP-led government stripped Jammu and Kashmir of its autonomy and brought it directly under the control of the union government. They have also split Jammu and Kashmir state into Jammu and Kashmir union territory and Ladakh union territory.
2020-The Nobel Corona Virus: The COVID-19 pandemic in India began on 30 January 2020, when the first case was reported in Thrissur.[123] In September 2020, India's health minister Harsh Vardhan stated that the country planned to approve and begin the distribution of a vaccine by the first quarter of 2021. Vaccination against COVID-19 started in India on 16 January 2021. By early April 2021, the second wave of infections took hold in the country with destructive consequences. The second wave placed a major strain on the healthcare system.
2021: India administered 1 billion doses of COVID-19 vaccine on 21 October 2021. On 72nd Republic Day on January 26, 2021, thousands of protesters entered Delhi on their tractors and wreaked havoc on roads, clashed with police, and even hoisted a religious flag from the ramparts of the iconic Red Fort, a privilege reserved for the Indian tricolor. The IMF on 12 November 2021 projected India’s growth at 9.5 percent in the current fiscal and 8.5 percent in the next fiscal. Both these are the highest growth rates in the world.
2022: Chief Minister Yogi Adityanath is the first in 37 years that a political party is winning for the second consecutive time in the state. Congress is in an existential crisis. It rules with a majority in just two states today, Rajasthan and Chhattisgarh.




